Filtration Ability Against Pressure
The coefficient of filtration ability against pressure shows the ability of the fluid to keep the initial characteristics even in the presence of pressure.

In case of heavy ingress of water, it’s better to go for a fast setting injection of resins. Generally, polyurethanes like
RESFOAM 1KM or
FOAMJET are better. Double component are faster in setting whereas the time of setting of Single component can be controlled if it has to be injected for a longer distance with an accelerator. Also, Nano Silica based injection material is used; it generally has particle sizes of less than 0.1 micron like the
Mapejet System NS15.
Colloidal silica gel is a “mineral grout” and not a chemical grout It is a stable liquid containing single, sub-microscopic particles of silica oxide. To make it gel, a weak solution of salt water is mixed prior to pumping. The more salt water added, the faster the gel time. It is environmentally friendly and durable, as it is simply composed of quartz sand, water and salt. Having the consistency of water, it penetrates sands and fine fissures very easily. It is extremely user-friendly as a standard cement grout equipment can be used and cleaned with water.
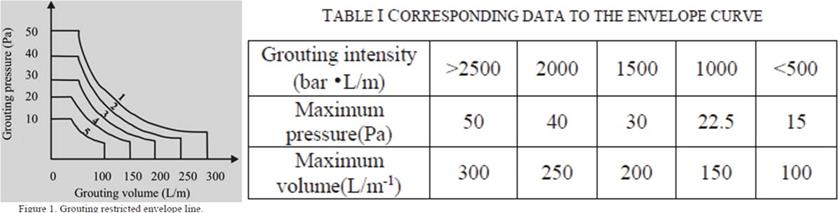
In Grouting the most important is the GIN (Grout Intensity Number). GIN grouting intensity values were defined as the product of the final grouting pressure and absorption per meter for a given single borehole, within a certain period at the end of grouting the result is a constant value.
GIN = PV
where P is the final grouting pressure and V is the ultimate grout take which means the energy consumption per unit grouting period
- Alluvial Soil Grout pressure: low, average 2-4 bar, maximum 7-10 bar
- Cracks in Rock Grout pressure: High, average 30-40 bar, maximum 70-80 bar
GIN value varies with different geological conditions, but GIN is constant under similar conditions. It needs to be noted that the GIN in each envelope curve includes a maximum pressure and maximum absorption slurry in addition to a GIN value. When the injection rate reaches a pre-determined limit, or pressure reaches the limit, or the product of the two factors achieve the selected GIN, the grouting can be ended.
Post Injection: Basic features
Reactive mindset: post-injection is conducted when collapses have occured already or uncontrolled water inflow is occuring; or where rehabilitation of leaking tunnels is required; or drilling holes to intersect joints with high water inflow, or pushing slotted pipes into unstable ground masses. These may need specialised drilling equipment such as Odex, Self drilling anchors and packer injections, utilization of expensive, highly reactive chemicals - usually PUs in geotechnical problems and acrylates in rehabilitation problems.
Single Component Polyurethane or Double Component Polyurethanes can be used, or Acrylates. To stop water ingress immediately the Polyurethane can be injected and then acrylates can be injected into joints or cracks. Various Tunnel linings have used the leakage control method with Polyurethanes like
RESFOAM /
FOAMJET and
Mapegel UTT.
Injection in fissures:
- Extremely low viscosity
- Resin should also be injectable when gelling has commenced
- Gelling properties, accurately adjustable
Technical solution for rehabilitation of old tunnels
- Acrylates for the injections in and immediately behind deteriorated concrete lining
- Polyurethane (Resfoam 1km) for the improvement of ground, void filling and water seepage reduction
- Taylored cement-based grout for improvement of ground behind concrete and masonry lining
- Sprayable waterproofing membrane on old tunnel lining
- Eventual sprayed concrete
Grouting is a design choice: Pre-injection vs Post Injection
Pre-injection – proactive, relies on effective probing and decision making at the face, cheap materials, 10 to 50 times then post, pre-injection often difficult in soft ground tunneling.
Post-injection – reactive, the last resort, expensive chemicals, unstable conditions and uncontrollable water inflows.
Make the right choice of materials for the right situation at the design stage. Mapei provides a complete system of Pre Injection and Post Injection for Civil Engineering Projects. Find out more information from
UTT Mapei.



